ONI frequency converters for lifting and crane equipment

In Russia, about 200 thousand cranes of various types are in operation: overhead, gantry, jib, tower, boom, portal, and mobile. Some of them have reached the end of their service life and require replacement, repair, or modernization.
When full replacement of outdated equipment is impossible, its modernization is necessary. How to do this with a frequency converter — we tell in the article.
The problem of updating and modernizing
lifting equipment
Manufacturers of modern cranes and hoists use various technologies: remote monitoring and control, energy saving, increasing operator and personnel safety.
However, the pace of updating lifting equipment in Russia is at a low level. According to EMISS data, the most cranes were produced in 2022 (6200 units), and now their production is at the level of 2021 (5800 units). Even with imports taken into account, the total volume of production and supply of new cranes and hoists annually does not exceed 8% of those in use. At the same time, old mechanisms fail and require replacement.
Thus, to completely renew the crane equipment base of the Russian Federation, as well as to commission new production facilities for lifting mechanisms, at least
Variable frequency electric drive
in lifting equipment
A modern way to increase the efficiency of cranes and hoists is to equip them with electric motors with frequency control. Modern frequency converters allow full use of automated control system capabilities, remote control of mechanism operation, and monitoring their condition.
Here are the main advantages of using VFDs for cranes and hoists.
- Precise positioning. Frequency converters allow controlling the speed and torque of the electric motor over a wide range and with high accuracy. This ensures smooth start and stop of the load with good positioning thanks to feedback. Deceleration to stop does not require a mechanical brake, which is especially important when working with fragile loads or performing complex, frequently repeated operations.
- Energy saving. By regulating the motor speed, frequency converters reduce the crane's energy consumption. This means reduced load on the grid and equipment wear.
- Safety. Modern frequency converters are equipped with safety functions (e.g., STO) and protect the motor from overloads and emergency situations. This prevents equipment damage and personnel injuries.
- Convenient maintenance. VFD is a compact, relatively simple to maintain device. It is placed in a separate control cabinet or container with a heating and air conditioning system.
Selecting a frequency converter

The choice of a suitable VFD depends on the specific requirements for the crane or hoist: lifting capacity, speed of movement, and operating conditions.
When choosing, it is necessary to consider the device's power, output current, frequency range, control accuracy, availability of safety functions and overload capacity, and correctly select external braking resistors and chokes.
It is necessary to distinguish between frequency converters for different tasks:
- VFDs for hoisting drive (e.g., ONI K751 VFD) must have high overload capacity, support operation in vector control mode with feedback, hold the load until the brake is applied, control torque, speed, and the mechanical brake, and have STO and anti-sway functions.
- VFDs for crane and trolley travel and rotation drive (e.g., ONI VFDs of series K750 and K740) must at a minimum ensure smooth motor start and stop, have speed limitation, possess good overload capacity, and handle limit switch states.
ONI frequency converter series
VFD K751 are designed to control a wide range of electric drives, as well as mechanisms with high starting loads. The main application area is lifting and crane equipment. The series includes 14 different sizes of three-phase versions with power from 0.75 to 710 kW in heavy-duty mode and output current up to 1260 A. The full-text LCD panel and special parameter group P59 allow safe and efficient control of the lifting mechanism and brake when moving the load, and the ability to connect an encoder/resolver allows precise load positioning.
These VFDs have proven themselves well in vertical movement and load holding and mechanical brake control, as well as when working with industrial hoists. They have overload capacity in heavy-duty mode up to 220% for 1s and starting torque of 200% at 0 Hz. Equipped with a Russian-language LCD screen with real-time mode support, built-in EMC filter C3, and support for industrial protocols.
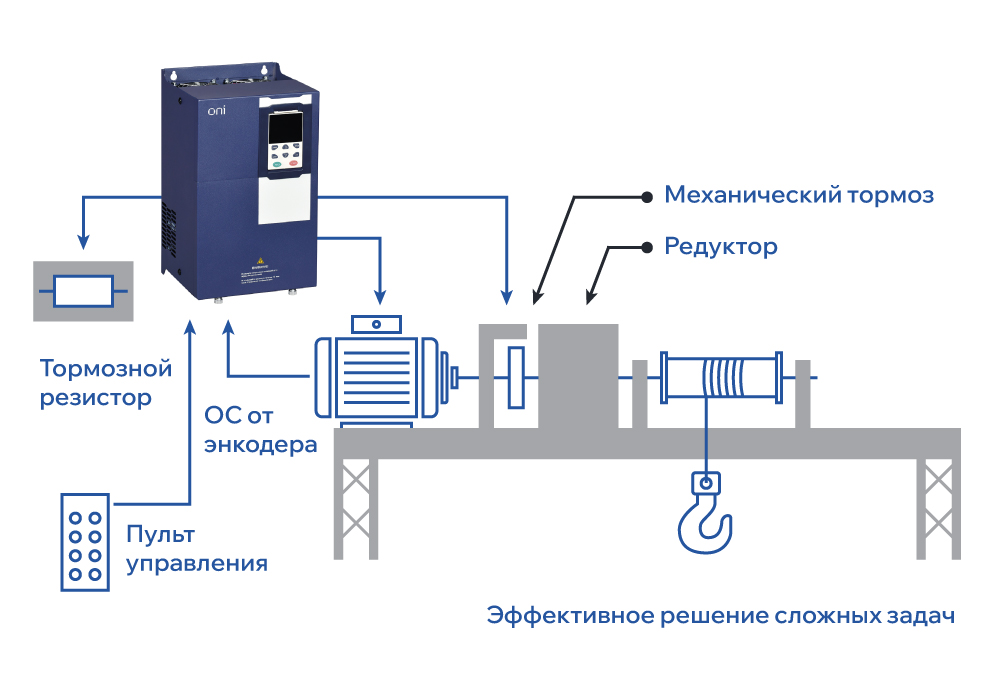
Fig. 1. Using K751 ONI for work with a lifting mechanism.
VFD K750 are designed for heavy-duty applications with vector feedback. They have a built-in Modbus protocol, support expansion boards (including encoder/resolver board, industrial protocol boards, e.g., Modbus TCP, CanOpen, Profinet). Used in various industries, utilities, and construction.
K750 are equipped with a Russified LCD display with a user-friendly interface. Comprehensive protection is provided for abnormal situations (overheating, motor overload, short circuit, overvoltage, etc.) and an STO function. In terms of technical capabilities, they are similar to the K751 series, except for the special parameter group for working with lifting mechanisms. Support for feedback, high overload, and the presence of PID regulation maximally expand the functionality and application area of K750.
VFD K740 are designed for critical applications in various industries, utilities, agriculture, and construction. A feature of the series is convenient and fast integration into the enterprise's industrial network due to the use of various protocols with the help of expansion boards (Modbus RTU, Profibus DP). The Profibus DP expansion board is initially built into the VFD K740 for corresponding articles.
The series includes frequency converters with a wide range of powers and voltages, including 690 V for industrial networks. VFD K740 are distinguished by good overload capacity and a large number of inputs/outputs. Integration into the industrial network is achieved by selecting the appropriate expansion board.
VFD K740 do not have specialized parameters for hoisting/lowering control but can be used for crane and trolley travel and rotation.
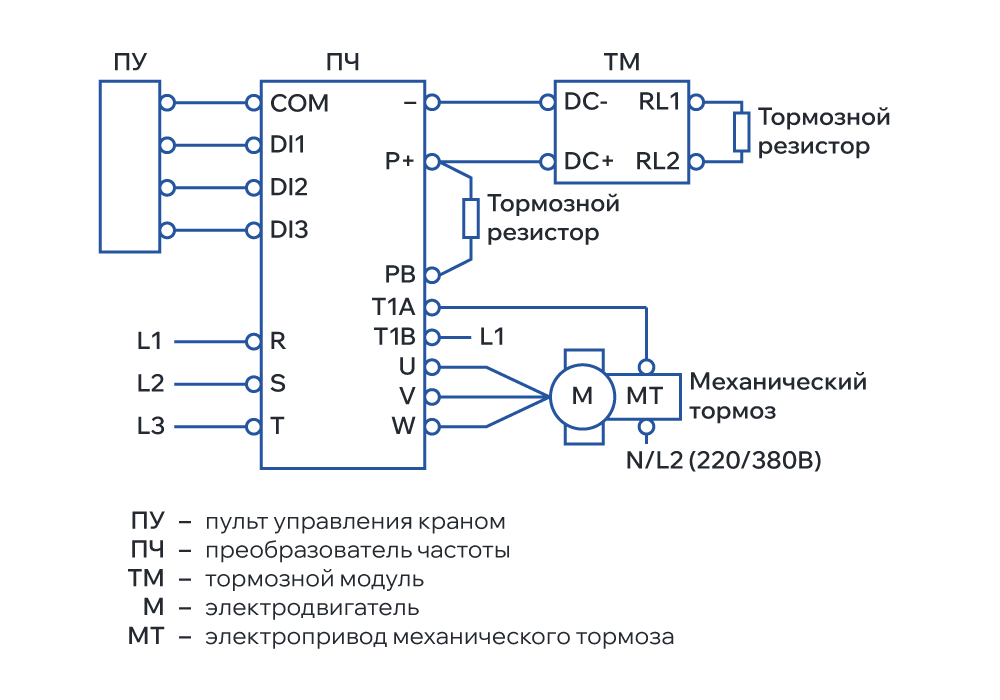
Fig. 2. Frequency converter K740 connection diagram.
Conclusions
In the crane equipment market in the Russian Federation, positive dynamics in meeting demand are emerging. In the future, they will depend, first of all, on the volumes of domestic equipment production replacing departed imports from Germany and Japan. Chinese manufacturers continue to hold a significant share of the crane equipment market.
Currently, crane equipment is produced in the Central, Volga, Northwestern, Southern, and Ural federal districts. Thus, the production and supply of modern lifting equipment cover the entire territory of Russia, which positively affects the renewal and modernization of outdated equipment.
Thanks to state support and targeted efforts of national producers, the domestic market has the potential to shift in favor of Russian companies. Specialized crane VFDs for hoisting or travel are in demand at present and constitute a significant share in industry or construction.
Still have questions? Ask ONI technical support specialists: support@oni-system.com, tel:


